Roof Pitch Calculator [Free] – Ratios, Degrees, and Slopes
Accurate roof pitch measurements are critical for professionals. The slope of a roof affects material takeoffs, labor needs, safety requirements, and compliance with building codes. Even a small mistake can lead to wasted time, wrong orders, or costly rework.
This free Roof Pitch Calculator gives contractors and subcontractors quick conversions between rise-over-run ratios, angles, and multipliers. It’s a practical tool you can use on site for checking measurements, preparing bids, and sharing specs with your crew or clients.
Alongside the calculator, you’ll find a roof pitch chart, key formulas, and practical guidance on when pitch matters most in construction.
Roof Pitch Calculator
What Is Roof Pitch?
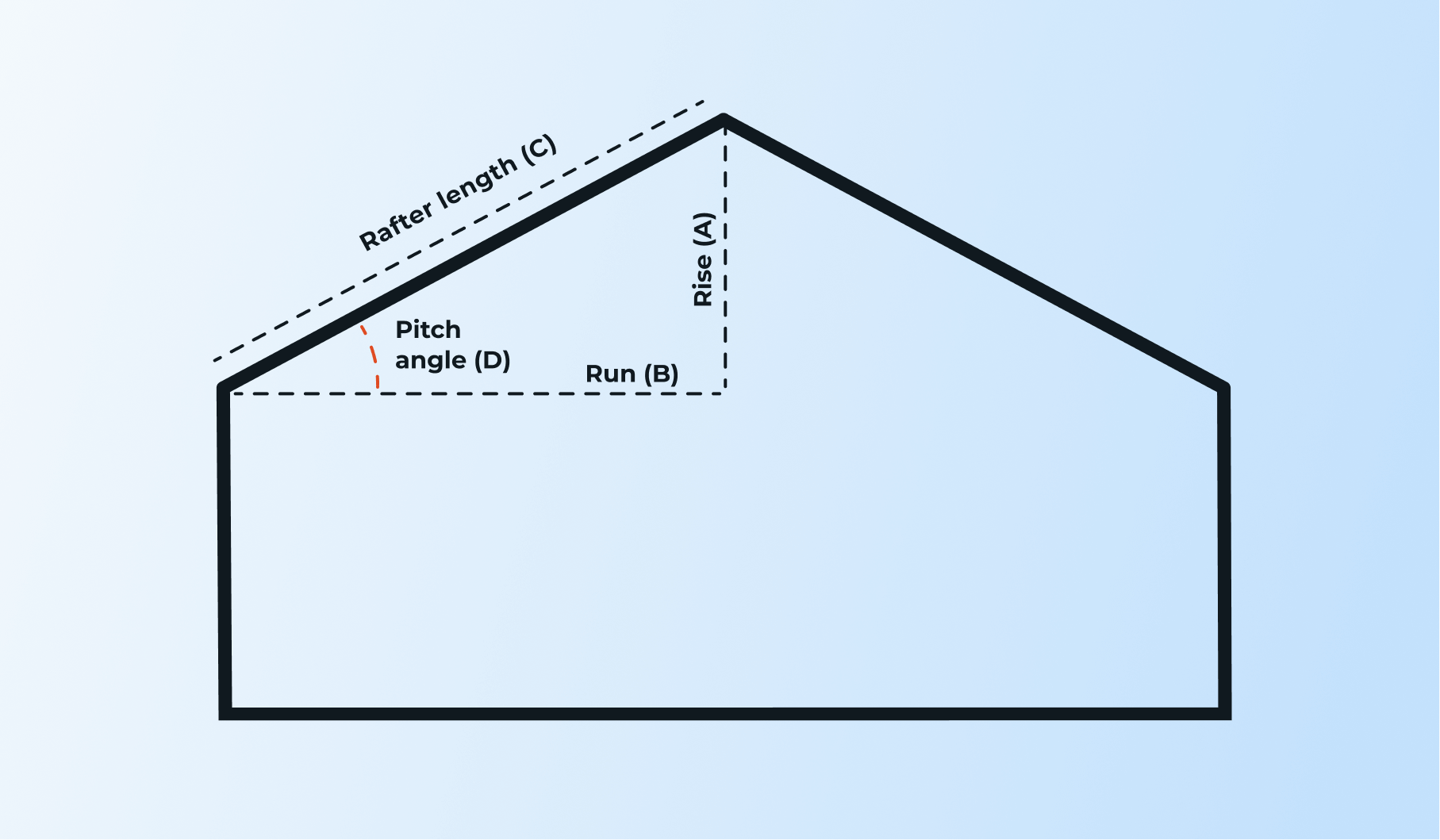
Roof pitch, also called roof slope, is the incline created by the rafters. It can be described in different ways:
- Angle in degrees compared to the horizontal
- Ratio of rise to run such as x:12 (common in North America)
- Percentage slope calculated as rise ÷ run × 100 (common in Europe)
Examples:
- 1:12 pitch ≈ 4.8° ≈ 8.3% slope
- 6:12 pitch ≈ 26.6° ≈ 50% slope
- 45° roof = 100% slope = 12:12 pitch
Roof pitch categories:
- Flat roofs → 0.5:12 to 2:12 (≈ 2% to 17%). Not perfectly flat; always include slight slope for drainage.
- Low-pitched roofs → below 4:12 (≈ 33%). Require special materials and careful detailing to prevent leaks.
- Conventional roofs → 4:12 to 9:12 (≈ 33% to 75%). Most common, efficient to build, safe to walk on with precautions.
- Steep or high-pitched roofs → above 9:12 (≈ 75%), sometimes up to 21:12 (≈ 175%). Great for snow and water runoff, but require extra fasteners, detailed crew planning, and strong safety controls.
For construction professionals, roof pitch is more than just geometry. It directly affects:
- Material estimating – steeper slopes increase surface area, which impacts tile, sheet, or membrane quantities.
- Structural design – slope influences how roofs handle rainwater, snow loads, and wind forces.
- Safety planning – steeper roof angles require scaffolding, fall protection, and additional crew planning.
- Compliance – building codes in many EU countries define minimum slopes for waterproofing systems (e.g., flat roofs often require at least 2–3% slope for drainage).
That’s why contractors rely on a roof pitch calculator or roof slope calculator to quickly convert between ratios, degrees, and percentages. For estimating, the roof pitch multiplier is especially useful to determine actual roof surface area from the ground plan.
How to Measure Roof Pitch on Jobsite
Roof pitch can be measured in different ways depending on regional standards. In Europe, it is usually expressed as an angle in degrees or a slope percentage. In North America, it is commonly written as a rise-over-run ratio such as x:12.
With a level and tape measure
- Place a spirit level horizontally on the roof.
- In Europe: mark a point 100 cm (1 m) along the level, then measure vertically from that point to the roof surface. If the rise is 30 cm, the slope is 30%, which equals about 16.7°.
- In North America: mark 12 in (30 cm) along the level, then measure the vertical rise. If the rise is 6 in (15 cm), the pitch is 6:12, which equals about 26.6° or 50%.
With a framing square or meter stick
- In Europe: align one leg with 100 cm horizontal run and read the rise on the vertical leg. This gives slope percentage directly.
- In North America: align one leg with 12 in of run, then read the rise on the vertical leg to get the pitch ratio.
With a digital tool
- Use an inclinometer, laser angle finder, or smartphone app.
- In Europe: read the angle in degrees, then convert to slope percentage if needed.
- In North America: read the angle in degrees, then convert to rise/run ratio with a roof pitch calculator.
Accuracy tips for contractors
- Take measurements directly on the roof surface for best results.
- Measure on more than one side of the roof to confirm consistency.
- When possible, measure from inside the attic to avoid safety risks on steep roofs.
Roof Slope Formulas and Conversions
Whether you’re working in percentages, degrees, or ratios, the math behind roof pitch is straightforward. Here are the key formulas used by contractors and subcontractors:
European approach (percent and degrees)
- Slope percentage = (rise ÷ run) × 100 Example: 30 cm rise over 100 cm run = 30% slope
- Angle in degrees = arctan(rise ÷ run) Example: 30 cm ÷ 100 cm = 0.30 → arctan(0.30) ≈ 16.7°
American approach (rise over run ratio)
- Pitch ratio = rise : run (standardized to 12 in run) Example: 6 in rise over 12 in run = 6:12 pitch
- Angle in degrees = arctan(rise ÷ run) Example: 6 ÷ 12 = 0.50 → arctan(0.50) ≈ 26.6°
- Slope percentage = (rise ÷ run) × 100 Example: 6 ÷ 12 = 0.50 → 50% slope
Roof pitch multiplier
The multiplier is used to calculate the true length of rafters or the actual roof surface area from the horizontal run.
- Formula: √(rise² + run²) ÷ run
- Example: For a 6:12 pitch → √(6² + 12²) ÷ 12 = √180 ÷ 12 ≈ 1.118
- Multiply the horizontal roof area by this number to get the true surface area.
Practical uses
- Estimating shingles, tiles, or sheet materials
- Calculating rafter lengths
- Determining drainage performance
- Comparing international specs (degrees ↔ ratios ↔ percentages)
FAQs About Roof Pitch for Contractors
What is the most common roof pitch?
Most residential projects fall between 30° and 40°, which is roughly a 6:12 to 8:12 pitch or a 50–67% slope. This range provides good water drainage while keeping construction straightforward and cost effective. If you need to check exact conversions for a specific project, a roof pitch calculator can give you instant results.
What roof pitch is considered safe to walk on?
Roofs under 20°, around a 4:12 pitch or 33% slope, are generally safe to walk on with the right footwear. Steeper roofs should always be treated as hazardous and require fall protection and proper crew management.
How accurate do roof pitch measurements need to be?
For estimating materials and preparing bids, a tolerance of about one degree or one centimeter per 100 cm of run is usually enough. For engineering and compliance purposes, always check the tolerances required by local building codes.
Can I convert roof slope percentage to pitch ratio?
Yes. A slope percentage can be converted to a rise-over-run ratio and then scaled to the American 12-inch system. For example, a 50% slope means 50 cm rise over 100 cm run, which equals a 1:2 ratio and translates to a 6:12 pitch.
How do I convert roof angle in degrees to slope percentage or pitch ratio?
To convert degrees, take the tangent of the angle. Multiplying it by 100 gives you the slope percentage. Multiplying it by 12 gives you the pitch ratio. For example, 30° has a tangent of about 0.577, which equals 57.7% slope or about a 7:12 pitch.
What is the minimum roof pitch for drainage?
Flat roofs should never be completely flat. Most codes in Europe require at least 2–3% slope, which equals about 1–2 cm rise per meter of run. In North America, this is often expressed as 0.25:12 to 0.5:12. This small incline ensures water runoff and prevents ponding.
What is the steepest roof pitch allowed?
There is no absolute maximum, but very steep roofs above 60° are rare outside of special architectural styles. In most modern housing, slopes between 25° and 50° are common. Pitches above 45° (12:12) require additional fasteners and careful safety planning for crews.
How do I find the roof pitch from plans or drawings?
Look for the section view where the rafter is drawn. The slope may be marked directly in degrees, as a percentage, or as a ratio such as 6:12. If only dimensions are given, divide the rise by the run and convert to the format you need.
What roof pitch is best for solar panels?
The ideal roof angle for solar depends on your latitude. As a rule of thumb, the roof pitch should be close to the latitude angle of the site. For example, in southern Europe at 35° latitude, a 30–35° roof pitch is near optimal. Flatter roofs can use racking to adjust the panel angle.
Does roof pitch affect cost?
Yes. Steeper roofs mean more surface area, more materials, and more labor. For example, a 45° roof has around 40% more surface area than a flat projection of the same span. This is where the roof pitch multiplier becomes useful in estimating.
What is the lowest roof pitch for tiles or shingles?
Most clay or concrete tiles require at least 15–20° slope. Asphalt shingles are usually rated for a minimum of 18.5° (3:12). Below these thresholds, water can seep under the covering, so special underlayments or membranes are required.
What is a roof pitch factor and how do I use it?
The roof pitch factor, also called the multiplier, is used to calculate actual surface area from the horizontal plan. Multiply the ground area of the roof by the factor to get true roof area. For example, a 6:12 roof has a factor of 1.118, meaning 100 m² of plan area equals 111.8 m² of roof surface.
How does roof pitch affect crew safety?
Low slopes can usually be walked safely, while anything above 20° requires care. Above 30° (7:12) fall protection systems, scaffolding, or roof ladders are essential. Managing who is on the roof, when, and with what equipment becomes critical. Many subcontractors use digital tools like Remato Crew Management to coordinate safety and schedules.
Why Roof Pitch Matters in Construction Projects
Roof pitch is not just a design detail. For contractors and subcontractors it affects almost every stage of a project, from estimating costs to ensuring crew safety. That is why many professionals keep a roof pitch calculator handy, both for quick checks on site and for preparing accurate bids.
Material estimating
The steeper the roof, the more surface area it has compared to the building footprint. A roof pitch calculator or roof slope calculator helps you apply the correct multiplier so you don’t under-order tiles, shingles, or membranes. Accurate takeoffs mean less waste and fewer project delays.
Structural performance
Roof slope has a direct impact on how a structure handles wind, rain, and snow. A shallow pitch may need special waterproofing systems, while a steep pitch requires additional fasteners and load considerations. Checking the numbers with a roof pitch calculator ensures your design matches the local conditions.
Safety and crew management
Steeper roofs increase the risks for workers. Anything above 30° (around a 7:12 pitch) often requires scaffolding, fall arrest systems, or roof ladders. Planning which tasks can be done safely on different slopes is easier when you know the exact numbers. Many subcontractors use digital tools such as Remato Crew Management to coordinate schedules and keep their teams safe on site.
Building codes and compliance
In many regions, minimum or maximum roof slopes are defined by code, often depending on roofing material. For example, flat roofs may require at least a 2% slope to meet drainage requirements. Using a roof pitch calculator lets you quickly confirm compliance while still on site or during the design stage.
Getting roof pitch right is essential for accurate estimates, code compliance, and safe crew management. Whether you are checking slope on site, preparing a bid, or planning materials, a reliable roof pitch calculator saves time and reduces costly mistakes.
Closing Thoughts
This guide covered how to measure roof slope, convert between ratios, degrees, and percentages, and why pitch matters in real projects. Keep this roof pitch calculator bookmarked so you always have the numbers at hand for your next job.
Once you have the pitch and surface area calculated, the next step is figuring out your project’s profitability. Our Profit Margin Calculator makes it simple to see exactly where your money is going and how much you will make on each job.
For subcontractors managing multiple teams and sites, accurate calculations are only part of the workflow. Tools like Remato Crew Management help you schedule crews, track work, and stay in control of complex projects.
